Preppers101Blog
Latest Post
When The Power Goes Out
Marcy Young
Southern Oregon Survival
http://www.preppers101.com
April, 16, 2016
Have you ever asked yourself what you would do if the power went out?
What if it was for a day or two or for a week or two…what if it was longer? Could you fend for yourself and your family? Could you keep yourself warm in the winter and cool in the summer? How would you keep your food cold and water flowing? What would you do about money if credit cards and ATMs no longer worked? How would you know how far reaching the power outage is and how would you receive important updates? How would you take care of your hygiene and sanitation issues? How would you put gas in your car? There is so much to consider when it comes to electrical power.

Our lives depend on it and most don’t know what to do without it.
We live in an electricity dependent infrastructure and once the electricity is down, so is our system.
A power outage is not something that just might happen.
I can pretty much guarantee that it will happen.
The U.S. electric grid is a complex network of independently owned and operated power plants and transmission lines. Aging infrastructure, combined with a rise in domestic electricity consumption, has forced experts to critically examine the status and health of the nation’s electrical systems.
A closer look at the threats
Cyber attack:
 Ted Koppel’s book – ‘Lights Out: A Cyberattack, A Nation Unprepared, Surviving the Aftermath‘- published in October, 2015 spells out what may be our nation’s greatest risk – a catastrophic shutdown of one or more U.S. power grids.
Ted Koppel’s book – ‘Lights Out: A Cyberattack, A Nation Unprepared, Surviving the Aftermath‘- published in October, 2015 spells out what may be our nation’s greatest risk – a catastrophic shutdown of one or more U.S. power grids.
According to the Forbes.com article ‘Major Cyber Attack On U.S. Power Grid Is Likely’ -A destructive malware app known as ‘BlackEnergy’ caused a power outage on the Ukranian power grid this past December, resulting in a blackout for hundreds of thousands of people. Ukranian officials have blamed Russia for the cyber-attack. A CNN article states that U.S. systems aren’t any more protected than those breached in Ukraine.
The U.S. national power grid faces physical or online attacks approximately “once every four days,” according to a new investigation by USA Today, threatening to plunge parts of the country into darkness.
Physical attack:
SAN JOSE, Calif.—The attack began just before 1 a.m. on April 16, 2013, when someone slipped into an underground vault not far from a busy freeway and cut telephone cables. Within half an hour, snipers opened fire on a nearby electrical substation. Shooting for 19 minutes, they knocked out 17 giant transformers that funnel power to Silicon Valley. A minute before a police car arrived, the shooters disappeared into the night.

Did You Know?
The U.S. has few high-power electrical transformers held in reserve, because of the multimillion-dollar price tag, and the delivery of new ones can take more than six months. This is under normal circumstances.
Radiation burst:
Either a man-made or natural event where a burst of electromagnetic energy is released. This attack is broken down further into two man-made attacks and one natural-occurring phenomenon:
-
An ElectroMagnetic Pulse (EMP)
When you tune your radio, watch TV, send a text message, or pop popcorn in a microwave oven, you are using electromagnetic energy.
Electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays.
A radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x-ray machine uses yet another portion.
Click on the following link to watch this recent video to get a good understanding of EMPs. Presentation by Dr. Peter V. Pry on EMP.

An EMP is a high-intensity burst of electromagnetic energy caused by the rapid acceleration of charged particles.
This results when a nuclear weapon explodes at high altitude.
An EMP has three main components:
- An electromagnetic shock disrupts electronics, such as communication systems;
- an effect similar to lightning rapidly follows and compounds the first component;
- the pulse flows through electricity transmission lines, overloading and damaging transmission distribution centers, fuses, and power lines.
How quickly the EMP E1 pulse is delivered affects the consequent damage.
The pulse length increases as one goes further from the peak field region, and this is another reason (besides the natural decrease of the E1 field strength) to expect somewhat less damage towards the periphery of the exposed region.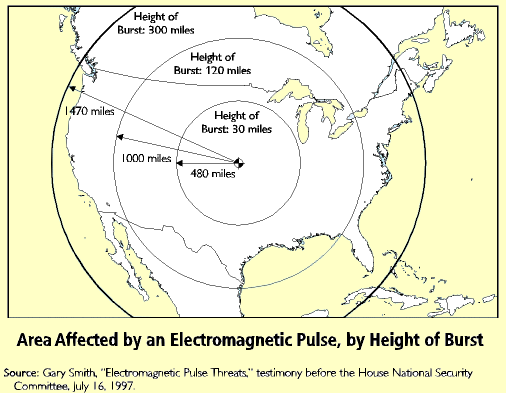
The easiest way to explain the results of an EMP are examining the items we use on an everyday basis. Microprocessors, other integrated circuits, transistors, diodes, etc. are semiconductors. (These parts make up virtually every electronic device).
Normally transistors and diodes have a decent tolerance to being overpowered, but when they are miniaturized to fit into integrated circuits and microprocessors, they become way more sensitive to overpowering.
That said, when the electromagnetic pulse induces current into the wires and components, the components get fried rendering the rest of the circuit useless.
There is a distinct lack of information available about EMP and its effects. Most of what we know is from nuclear tests, both American (Starfish Prime) and Soviet, in the 1960s. Starfish Prime was a high-altitude nuclear test conducted by the United States on July 9, 1962. It produced a yield equivalent to 1.4 megatonnes of TNT. It was the largest man-made nuclear explosion in outer space.
Starfish Prime caused an EMP, which was far larger than expected, so much larger that it drove much of the instrumentation off scale, causing great difficulty in getting accurate measurements. The Starfish Prime EMP also made those effects known to the public by causing electrical damage in Hawaii, about 898 miles away.

In the U.S. Starfish Prime event, the maximum electric field pulse experienced was in the range of 5,000 to 5,600 volts per meter.
During Soviet tests over Kazakhstan in 1962, rugged diesel generators having no solid state parts were burned out by E1 EMP. The Soviet tests were as high as 10,000 volts per meter.
It is possible to rather easily generate 50,000 volts per meter with an old second-generation nuclear weapon of the proper design. There are reports that it may be possible to make nuclear weapons that will push beyond this 50,000 volts per meter limit.
An EMP of 50,000 volts per meter would undoubtedly damage some cars, both with and without solid-state electronics. What percentage of vehicles would be damaged, and which particular vehicles would be damaged, is something that even the best EMP experts can only make guesses about. The total available data is just too limited, and the number of variables are huge.
The worst thing about nuclear EMP and motor vehicles is if you happen to be driving in heavy traffic when it happens.
 In this event, simultaneously, a certain percentage of vehicles will stop running (perhaps temporarily), many more drivers will be instantly and simultaneously distracted by strange electrical behavior happening inside of the car, and (at the same instant) the traffic lights will abruptly go out or go into a flashing mode.
In this event, simultaneously, a certain percentage of vehicles will stop running (perhaps temporarily), many more drivers will be instantly and simultaneously distracted by strange electrical behavior happening inside of the car, and (at the same instant) the traffic lights will abruptly go out or go into a flashing mode.
This instantly creates the worst traffic jam in history. If you have a working motor vehicle in a post-EMP situation, there may not be any clear roads to drive on.
Go to Preppers101Blog for article: EMP Effects On Vehicles
- A Directed Energy Weapon is similar to an EMP. However, the energy burst is more focused and does not need a nuclear detonation. Being portable and less a technological challenge, this type of attack is a concern.
- Geomagnetically-Induced Currents are the results of a Coronal Mass Ejection or a severe solar storm. The radiation emitted alters the Earth’s magnetic field and can induce currents in transmission lines that can destroy electrical equipment.
On September 1, 1859, the largest recorded geomagnetic storm occurred. Telegraph systems all over Europe and North America failed, in some cases shocking telegraph operators. Telegraph pylons threw sparks and telegraph paper spontaneously caught fire.
EMP PROTECTION:
Despite the EMP Commission’s recommendations in 2004 and 2008, hardly any progress has been made in protecting the country from an EMP attack and its catastrophic results.
The U.S. military hardens many of the country’s strategic defense systems against EMP effects but little is done to implement measures to protect civilian infrastructure.
Frequency List:
Starting with the lowest and the easiest for a Faraday cage to handle:
Solar flares and resulting geomagnetic storms: Hundredths of a Hz. Non-issue for electronics, absolutely no RF risk (i.e. if it’s not plugged in, it doesn’t give a damn).
Lightning: Mostly below 1 MHz. That means wavelengths of hundreds of meters, so anything that more or less surrounds your electronics will protect from the electromagnetic waves. (direct hits are a different animal) For testing in this frequency range, try an AM radio tuned to the strongest station you can find.
Nuclear EMP: Worst below 100 MHz, but significant up to several hundred MHz. Wavelengths as short as several inches. This is where things become demanding. Gaps of several inches in length may allow RF to penetrate into a Faraday cage. Making sure the lid contacts the body around its whole circumference, or at least every couple of centimeters, is important. To test isolation for this sort of thing, try at least UHF (FRS/GMRS radios operate around 460-470 MHz).
Non-nuclear EMP bomb: Up to several GHz, perhaps tens of GHz. Wavelengths down to a couple of centimeters.
Building a Faraday Cage
You can use any metal canister of any shape or size, but copper is the best. Lined with nonconductive material like cardboard, towel, bubble wrap, etc. Make sure there is no interruption of metal exterior with anything non-metallic. For example, a rubber gasket along the lid.
Layer electronics at least three times. For example: wrap radio in towel and place in mylar bag. Wrap mylar bag in towel and place inside second mylar bag. Place radio with doubled mylar inside a metal garbage can that is lined with cardboard. Seal metal can with metal tape.
If using screen mesh, one rule of thumb often used for Faraday cages to prevent transmission is that the holes need to be no larger than 1/10 of the wavelength of the signal. To take the guesswork out, It is BEST to use solid metal.
Let’s not forget severe weather, vehicle accidents, or even small animals climbing on pieces of equipment that can cause disruptions in power.
Some of you may figure you’ll be fine as long as you’ve got your generator and your gasoline. A generator serves its purpose- Short Term Power. A few hours or a few days are fine. By week two you’ll suddenly become a beacon in the night with your noisy power.
What you need is power that is quiet, reliable and self-sustainable. You can achieve this by using solar, wind, hydro, or biogas. Now I don’t suggest you put all your eggs in one basket and only invest in one form of power. Diversity is the key.

Goal Zero portable solar products provides unlimited power for work and home, without the noise, fumes, or cost of traditional backup generators.
1. SOLAR POWER is produced by collecting sunlight and converting it into electricity.
Photovoltaic (PV) modules make electricity from sunlight, and are marvelously simple, effective, and durable. They sit in the sun and, with no moving parts, can run your appliances, charge your batteries, or make energy for the utility grid.
To use the energy from the array, you also need other components, such as inverters, charge controllers and batteries. The components required are dependent on the system type designed. System types include:
PV-DIRECT SYSTEMS: These are the simplest of solar-electric systems, with the fewest components (basically the PV array and the load). Because they don’t have batteries and are not hooked up to the utility, they only power the loads when the sun is shining. This means that they are only appropriate for a few select applications, notably water pumping and ventilation—when the sun shines, the fan or pump runs.
OFF-GRID SYSTEMS: These systems operate independently from the grid to provide all of a household’s electricity. These systems require a battery bank to store the solar electricity for use during nighttime or cloudy weather, a charge controller to protect the battery bank from overcharge and an inverter to convert the DC power to AC for use with AC household appliances.
GRID-TIED SYSTEMS WITH BATTERY BACKUP: This type is very similar to an off-grid system in design and components, but adds the utility grid, which reduces the need for the system to provide all the energy all the time.
GRID-TIED SYSTEMS WITHOUT BATTERIES: These most common PV systems generate solar electricity and route it to the loads and to the electric utility grid, offsetting a home’s or business’s electricity usage.
Living with a grid-connected solar-electric system is no different than living with utility electricity, except that some or all of the electricity you use comes from the sun.
The drawback of these batteryless systems is that they provide no outage protection—when the utility grid fails, these systems cannot operate.
2. HYDROPOWER is power derived from the energy of falling water, which may be harnessed for useful purposes. Since ancient times, hydropower has been used for irrigation and the operation of various mechanical devices, such as watermills, sawmills, textile mills, dock cranes, domestic lifts and paint making.
3. WIND POWER, as an alternative to fossil fuels, is plentiful, renewable, widely distributed, clean, produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation and uses little land. Any effects on the environment are generally less problematic than those from other power sources. For more information, go to: www.awea.org
4. BIOGAS typically refers to a mixture of different gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Biogas can be produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste or food waste. It is a renewable energy source and in many cases exerts a very small carbon footprint. Some gasoline engines are designed for or can be modified for use with natural gas, propane or biogas. Diesel engines can accept up to 80 percent biogas. For a DIY article on making your own biogas, go to the Preppers101 Blog Site.
Here are some tips for preparing for a power outage:
WATER:
- Store at least 1 gallon of water per person per day for emergencies. Don’t forget water for your pets, gardening, sanitation and hygiene.
- Move frozen water bottles from the freezer to the refrigerator to keep it cool. Once thawed they can be used for drinking.
- Install a hand pump on your well to retrieve water during power outages.
- Build or purchase a solar water heating system for hot water.
LIGHTING, HEATING & COOLING:
- Have flashlights ready in multiple easily accessible locations around your home. Battery powered lanterns and headlamps are good for hands-free lighting. Be sure to also have plenty of fresh spare batteries. Consider using rechargeable batteries and having a solar powered battery and phone charger.
- Have emergency candles, matches,oil lamps, or propane lanterns, plus extra oil or fuel on hand. Use them carefully to prevent fire.
- Have plenty of split wood and kindling for your fireplace, woodstove, or outdoor fire pit for lighting, heating, and cooking.
- Learn how to make an air conditioning unit for your home that runs off of no electricity. Go to our YouTube channel, click on DIY projects.
FOOD STORAGE AND COOKING:
- Fill the empty space in your freezer with containers of water. Frozen water will displace air and keep food cold longer if the power goes out. Remember to leave space in containers for ice to expand. Once the power goes out move some of the frozen water bottles into the refrigerator to keep food cool.
- Do not open refrigerators or freezers any more than necessary. An unopened refrigerator will keep food cold for approximately 4 hours and an unopened freezer will keep food frozen for approximately 24 hours and even longer if it is located in a cold garage. You will need to throw away any food items that become warmer than 41 degrees.
- Cook perishable foods FIRST. If the temperature rises, take anything out of the refrigerator that might spoil and prepare to cook it or consume it before it warms up. Eat perishables before spoilage can occur.
- Learn alternative cooking methods like using a sunoven, dutch ovens, and how to cook over an open fire using charcoal or wood.
- Make sure you have a manual can opener for opening cans of food.
- If you are a coffee drinker have a French press and pre-ground coffee.
- Be wary of the possibility of carbon monoxide poisoning, which is caused from exposure to odorless fumes created by charcoal grills, camping stoves or generators that are operated inside a home or garage. Never, ever burn charcoal or use gasoline or propane-powered equipment inside your home. Don’t even do it in your garage or on your porch. Use such equipment only when you’re completely outdoors.
- Make a cold storage like a root cellar and refrigeration pot (zeer pot).
- Learn how to preserve meat through smoking and salting. Stock up on hundreds of pounds of salt.
COMMUNICATIONS:
- Have a battery-operated, solar or hand crank emergency radio so that you can stay in touch with the world. Make sure your radio is in working condition by testing it periodically.
- If you use a landline, have at least one phone with a handset cord in your home. Many cordless phones will not work in a power outage. Cell phone users should keep their cell phones charged and at the very least, pick up a cell phone car charger so you can charge the cell in your car if it runs down.
- Know where your local phone booths are in case cell phones are down and keep a good supply of coins in your car or bug out bag for making calls.
- Create a plan with your family in case of an emergency. Figure out where to meet and who to contact before the emergency takes place.
- Keep a ham radio at home and in your faraday cage for two-way communications.
TRANSPORATION:
- If you have an automatic garage door opener, learn how to use the manual release to open your garage door manually. Keep the instructions handy – perhaps taped to the inside of a closet door – so you don’t have to search for them when the time comes.
- Keep your automobile’s fuel tank at least half full. Many gas stations will not be in operation during a power outage. And please – fill up your tank if a major storm is predicted and keep extra fuel on hand for your generator.
- Know alternate routes home.
HYGIENE & SANITATION:
- Keep extra water stored just for hygiene and sanitation purposes. Keeping clean is very important during an emergency to prevent illness.
- Have a solar shower on hand and take a shower or bath once a day (even if it’s a sponge bath).
- Create a hygiene & sanitation kit that includes a portable toilet, toilet bags, and extra hygiene and sanitation supplies all in one location.
- Keep your nails cut short to keep bacteria from accumulating under them.
- Stock up on baby wipes for keeping clean while using little to no water.
MEDICAL & FINANCIAL:
Disaster Registry at www.preppers101.com, Rogue Valley Disaster Registry
- Notify your power company in advance if you use special healthcare equipment like oxygen generators or dialysis equipment that requires power. Most power companies have the ability to note this in their records and will prioritize the response to your home.
- Keep an extra supply of prescription drugs, eyeglasses, and medical supplies at home in case you are stuck at home and emergency services cannot get to you quickly.
- Learn how to grow and use herbal remedies.
- Keep cash and coins on hand. Once the power goes out you may not have access to ATM’s or credit cards.
- Diversify your investments. Investing in gold, silver, tangible goods, real estate, and skills will pay off greatly once the dollar is worthless or you just cannot retrieve it.
POWER:
- Once the power goes out, unplug sensitive electrical equipment such as computers, printers, televisions, and audio equipment. When the power comes back on, there may be power spikes that can damage delicate electronics.
- Turn off any natural gas coming into your house.
- If your budget allows, acquire a portable generator. Learn to safely use your generator and test it monthly. And don’t forget to store enough fuel to run the generator for up to a week. Remember, your portable generator does not have to run full time. Your refrigerator will be just fine without power over night when it is not being opened and closed repeatedly. If you do not want to rely on gasoline powered generators you can use solar powered generators.
KIDS:
- Keep a supply of books, board games, playing cards and other items available to keep you or your children entertained and amused during a power outage.
- Power outages can be scary for some children. Keep items on hand that will sooth and calm them like a piece of gum, music, or teddy bear.
- Practice power outages with your children. Start with one hour and work your way up to an entire weekend. Make it fun and productive.



You must be logged in to post a comment.